How to find Amps from KVA ? How to Convert KVA to Amps in Generator Asad Electrical YouTube

Converting Amps to kVA is a crucial task in electrical engineering and power management. With the Amps to kVA Calculator and the provided formula, you can easily perform this conversion. Whether you're designing electrical systems, managing power loads, or simply curious about electrical units, this tool simplifies the process and ensures.
Calculadora De Amperios A KVA ¿La Forma Correcta De Convertir Amperios A KVA? Electrositio
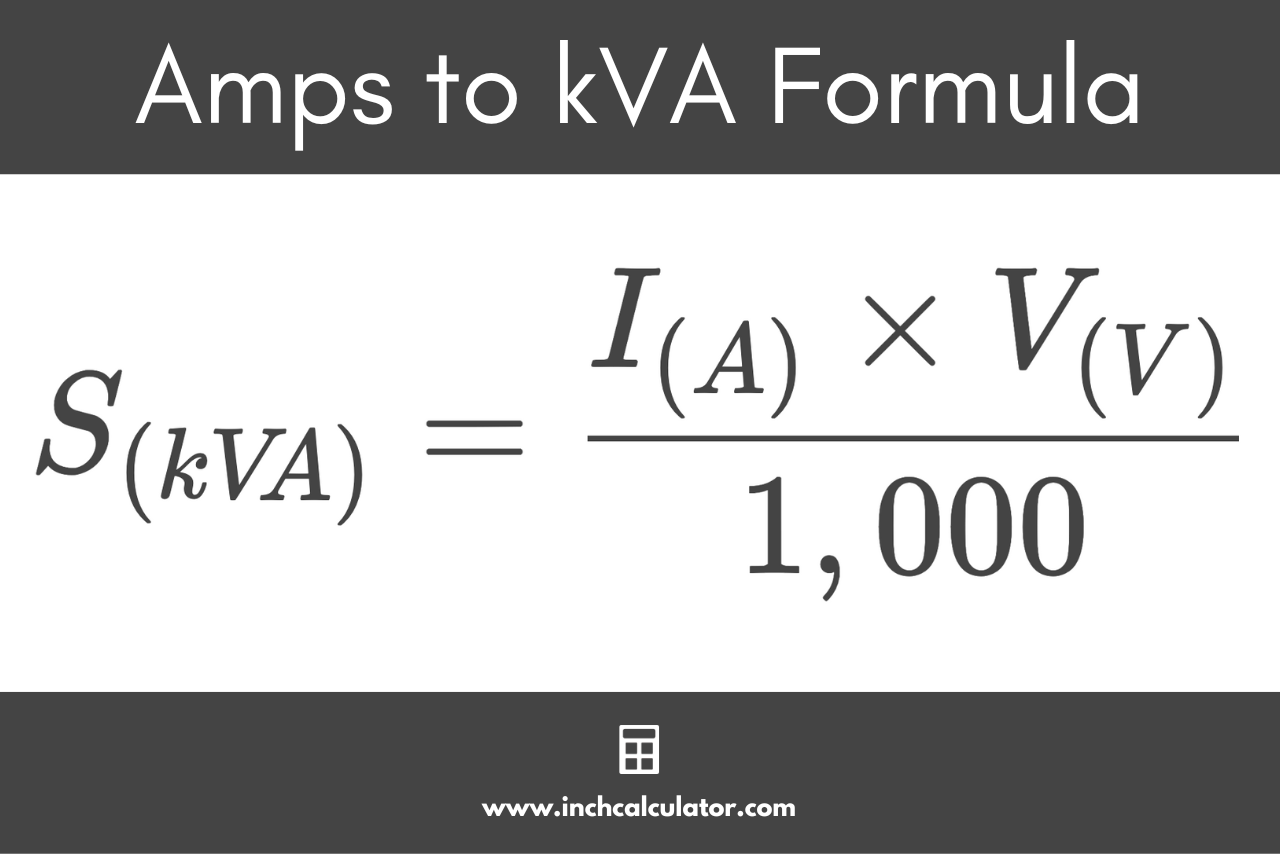
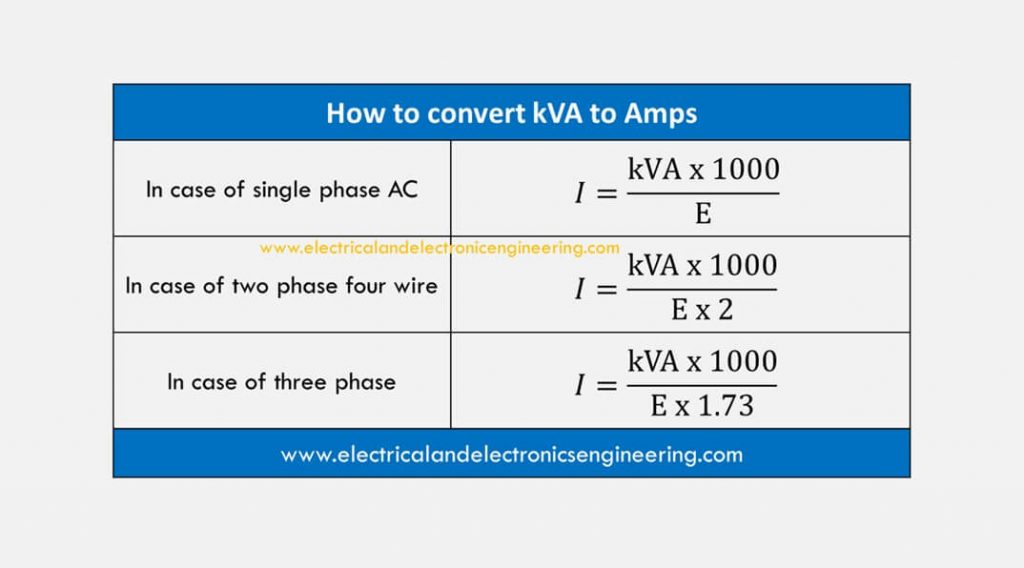
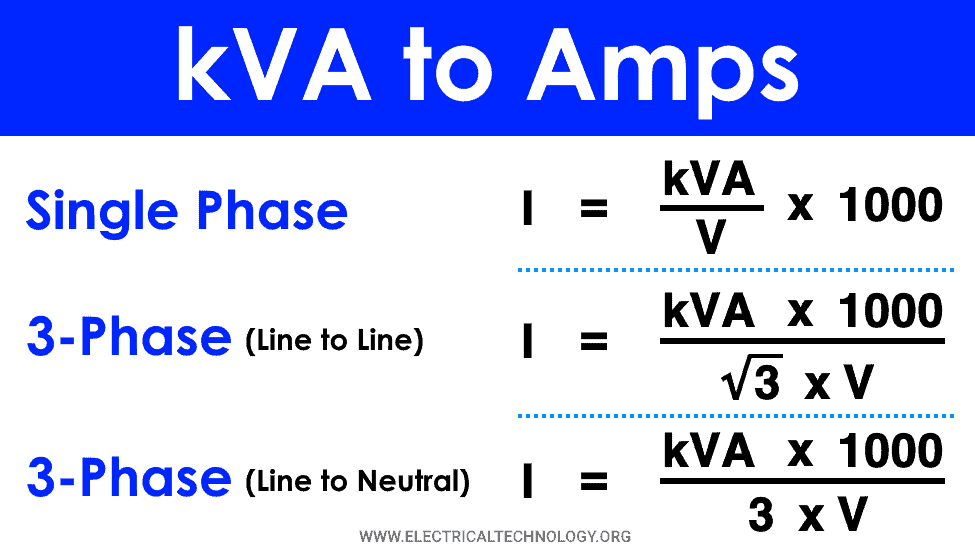
The formula to convert kVA to amps in a three-phase circuit looks like this: I (A) = S (kVA) × 1,000 / √3 × V L-L(V) For a balanced load where the current is the same on all phases, the current I in amps is equal to 1,000 times the apparent power S in kVA divided by the square root of 3 (1.732) times the line to line voltage V.
☑ Convert Capacitor Calculator

Amps (A) = (8 kVA x 1000) / (240 V x 0.9) Amps (A) = 33.33 A In this example, the load has an amperage of approximately 33.33 amps. It's important to note that the power factor (PF) plays a significant role in the calculation, as it represents the ratio of real power to apparent power.
conversion/kva to kw/kva to amps /kw to amps YouTube

1 kVa to amps (120V) = 8.33 A. 1 kVa to amps (220V) = 4.55 A. 1 kVa to amps (12V) = 83.33 A. Below the calculator, you will find a kVA to amps table (you have to know the voltage - usually 220 V), as well as 2 solved examples of how to convert kVA to amps. You can use it here:
Convert Kva To Kw slide share
Reset. Effortlessly convert Kilovolt-amps (kVA) to Amperes (A) using our user-friendly online converter. A kVA (Kilovolt-amps) corresponds to a power unit equal to 1,000 volt-amperes. Voltage represents electrical pressure, while amperage, denoted as amperes (A), signifies electrical current. This current can flow in single-phase, two-phase, or.
Amps to KilovoltAmps (kVA) Electrical Conversion Calculator
kVA to Amps Calculator. The following kVA to Amps conversion calculator will convert the apparent power "S" (i.e. kilovolt amperes or kVA) into current "I" in amperes "A", kiloamperes "kA", milliamperes "mA "and megaampere "MA".. To calculate the amperage rating of a device from the kVA rating, just enter the value of apparent power in kVA, voltage in volts, select.
Generator Ratings (back to basics)
Formula of calculating three-phase (kVA) to Amps. Line to line voltage. I (A) = 1000 x S (kVA) / (√3 x V L-L (V)), which means that the phase current in amps is calculated by multiplying 1000 by the apparent power in kilovolt-amps dividing the result by the square root of three multiplied by the line to line voltage RMS in volts.
CONVERSION kVA Ampères BD Consult Energie
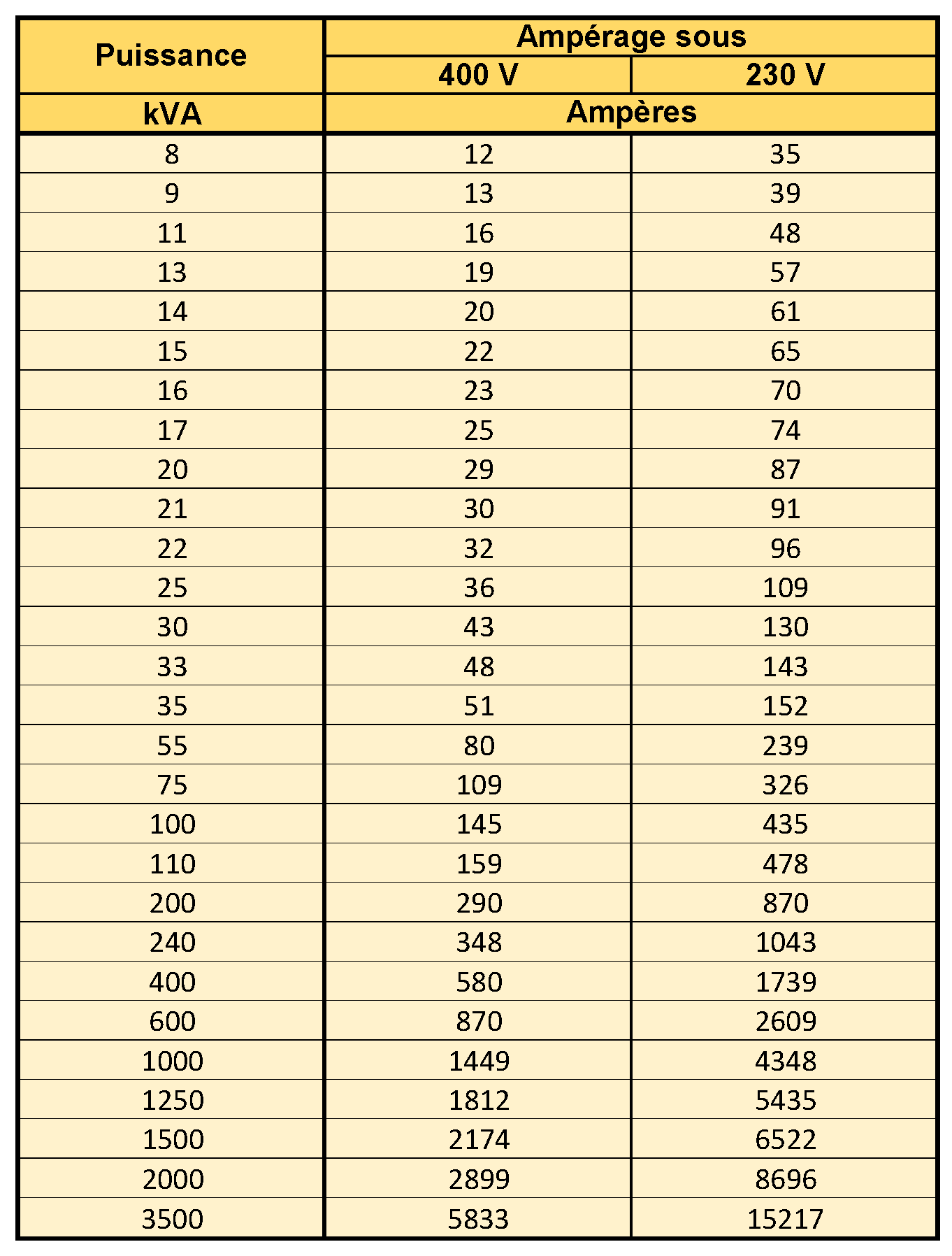
Single Phase kVA to Amps. The current in 1 φ circuits is a ratio of 1000 times kVA to voltage. Mathematical formula: I = [kVA * 1000] / V. Example: Find the amount of electric current flowing through a 200 volt, 5 kVA generator. Solution: I = [5 * 1000] / 200 = 25 A. 100 kVA to Amps. Example: Convert single phase 100 kVA, 3.3 kV to Amps
KW to KVA & Watts Conversion Calculator Online Generators Zone
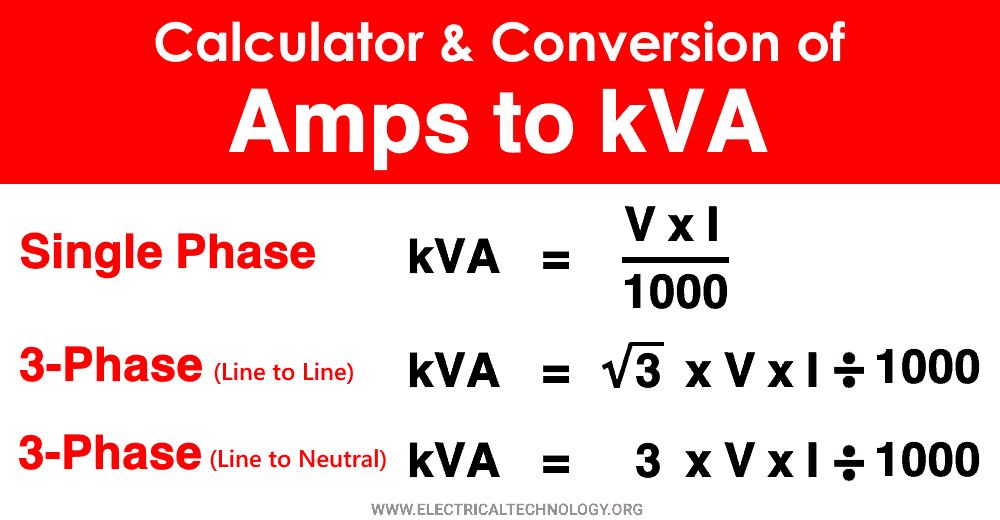
To convert amps to kVA in a single-phase power system, you can use the formula S = I × V / 1000 where the amperage (I) is in amperes, the voltage (V) is in volts, and the resulting apparent power (S) is in kilovolt-amperes or kVA. On the other hand, for the 3-phase system, you can use S = I × V × √3 / 1000 for line-to-line voltage and S.
How To Convert Amps To KVA PDF

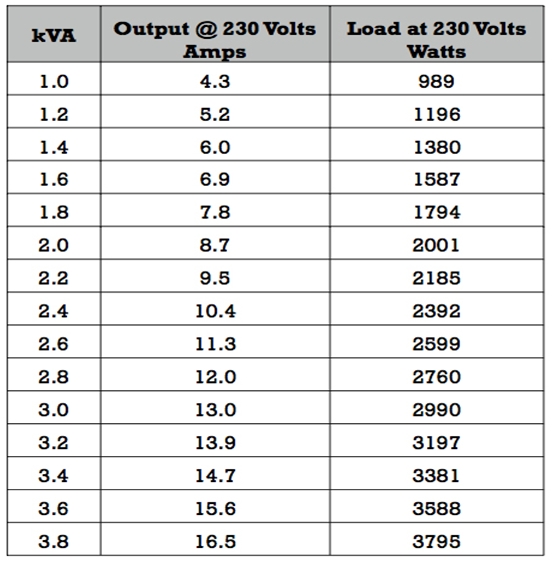
Kilovolt-amps to amps conversion calculator and how to calculate.. Enter volts: V Result in amps: A: kVa to amps conversion table. kVa Amps Volts; 1 kVa: 8.33 amps: 120 volts: 2 kVa: 16.67 amps: 120 volts: 3 kVa: 25.00 amps: 120 volts: 4 kVa: 33.33 amps: 120 volts: 5 kVa: 41.67 amps: 120 volts:
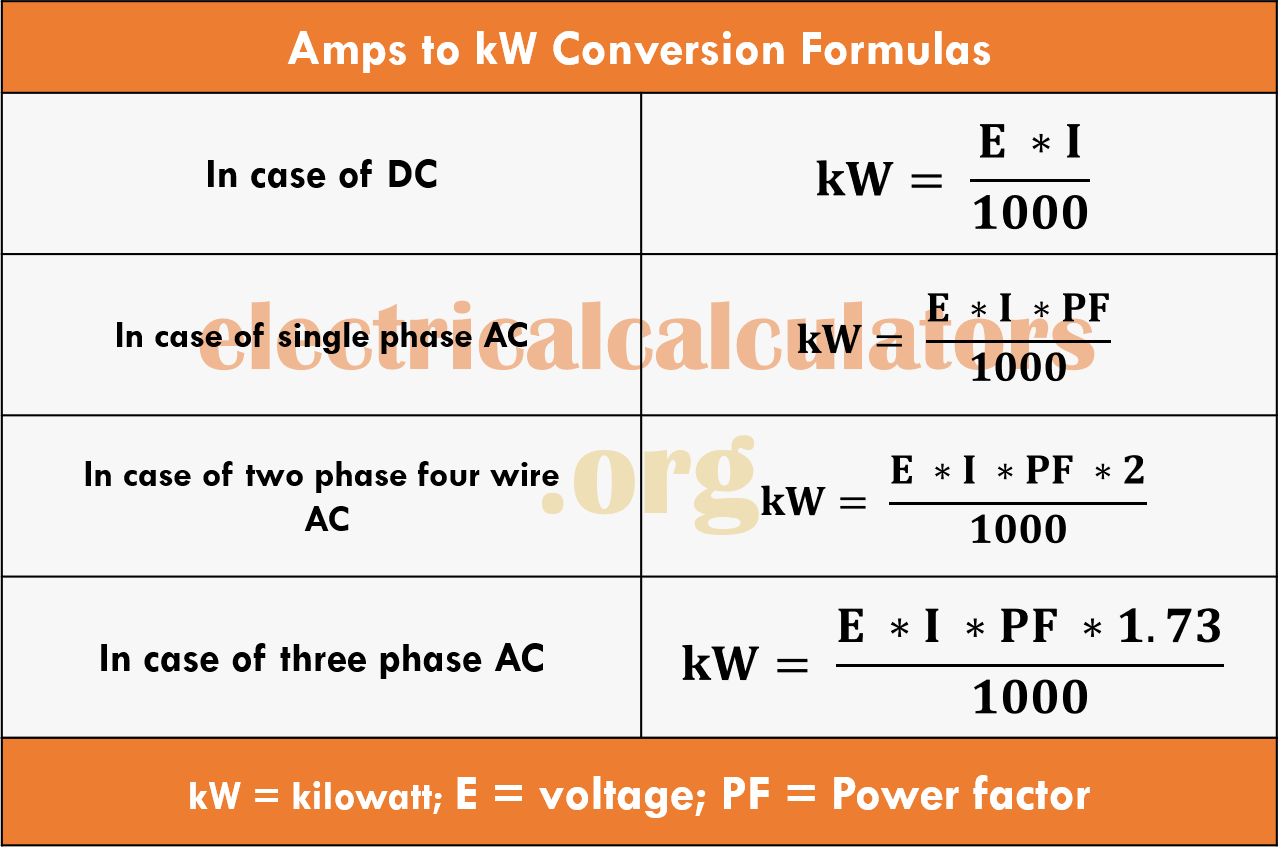
Amps to kW Conversion Calculator Formulas with Solved Examples in Case of Single, Two, Three
Our kVa to amps calculator simplifies the intensive task of converting kVa to amps, so you can get accurate results in time. Whether you are an engineer, electrician or just curious about your energy needs, our efficient tool is the go-to solution. Try our kVa to amps conversion tool today and make your energy projects a breeze!
kVA to Amps Conversion Formula Electrical and Electronics Engineering
Kilovolt-amps, abbreviated as kVA, is the typical unit of measure for what is called apparent power.Apparent power is the amount of electrical power produced by an electrical system at a particular applied voltage and current. Following the Ohm's law formula, we can obtain the amount of electrical power by multiplying the amount of voltage by the current flow through any electrical system.
Amps to kW Conversion Formula with Solved Examples [Video]

3 phase kVA to amps calculation formula Calculation with line to line voltage. For balanced loads, the phase current (I) in amps can be calculated by multiplying the apparent power (S) in kilovolt-amps by 1000. Then, divide the result by the product of the square root of 3 and the RMS line-to-line voltage (VL-L) in volts.
how to convert kva to va electrical calculation YouTube

Enter the apparent power in kilovolt-amps (kVA), voltage in volts (V), then press the Calculate button to get the result in amps (A). Single phase kVA to Amps calculation kVA: Voltage (V): Calculate Amps: 0 I(A) = 1000 × S(kVA) / V(V) The current I in amps (A) is equal to 1000, multiplied by the apparent power S […]
kVA to Amps Conversion Calculator Online Easy Rapid Calcs

The phase current I in amps (with balanced loads) is equal to 1000 times the apparent power S in kilovolt-amps, divided by 3 times the line to neutral RMS voltage V L-N in volts: I(A) = 1000 × S(kVA) / (3 × VL-N (V) ) kVA to amps calculation . Kilovolt-amps (kVA) to amps (A) conversion calculator and how to calculate.
kVA to Amps Calculator How to Convert kVA to Amps?
The kVA to Amps Calculator is a handy tool designed to help you convert electrical power from kilovolt-amperes (kVA) to amperes (A). In electrical systems, kVA represents the total power consumed or supplied by a circuit, considering both the actual power used (kW) and the reactive power (kVAR).
.